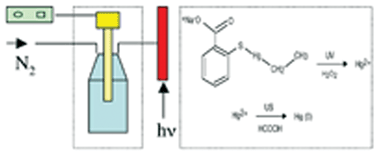
Greener analytical method for determination of thiomersal (sodium ethylmercurithiosalicylate) in ophthalmic solutions using sono-induced cold vapour generation-atomic absorption spectrometry after UV/H2O2 advanced oxidation
Abstract
A new method is described for the determination of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...