Vaporization and ionization of laser ablation generated aerosols in an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer—implications from ion distribution maps
Abstract
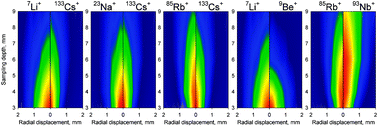
The distribution of elemental ions in the plasma of an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...