Detection of microalgae superoxide dismutase (SOD) using a GNRs-based resonance light scattering system
Abstract
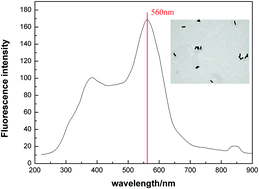
A novel and label-free, gold nanorods (GNRs)-based resonance light scattering system assay has been developed for the detection of microalgae superoxide dismutase (SOD). The method relies on the fact that interactions between microalgae SOD and GNRs can emit strong fluorescence signals. The prepared GNRs were well dispersed in the solution and intracellular SOD was extracted from Microcystis aeruginosa; the SOD was then absorbed on the surface of the GNRs. The results demonstrated that the intensity of the fluorescence signals increased at 595 nm with an increase in the SOD concentration, the optimum pH value was concluded to be 7.8, the optimum concentration of inorganic salt Na+ ions was 0.2 mol L−1, and the reaction system was stable for 50 min. This method offers the advantages of higher sensitivity and selectivity in microalgae protein detection and exhibits great potential for biological diagnosis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...