Enrichment of glycopeptides using environmentally friendly wood materials†
Abstract
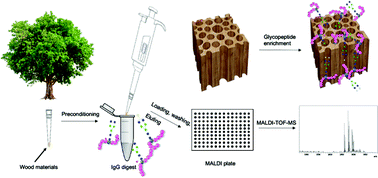
Glycoproteomics is one of the main routes to study protein post-translational modifications, and enrichment is one of the important steps. Many hydrophilic materials have been used for glycopeptide enrichment, however involving complex synthesis procedures, high consumption in cost, time, and chemicals. Here, balsa wood, a naturally available hydrophilic material with highly porous structure, was investigated for immunoglobulin G (IgG) glycopeptide enrichment in a micropipette set-up. Native balsa wood without any pretreatment provided a green alternative to a commercial HILIC product, exhibiting comparable, or even better, enrichment performance for IgG standard and human plasma IgG samples. After delignification, binding capacity and recovery could be improved due to increased hydrophilicity and porosity. The developed method utilizing wood materials introduced an environmentally friendly option for glycoproteomics, saving both costs and chemicals, while exhibiting high performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...