Iron-catalyzed cross-dehydrogenative coupling of indolin-2-ones with active methylenes for direct carbon–carbon double bond formation†
Abstract
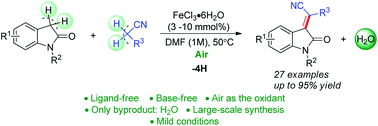
The iron-catalyzed cross-dehydrogenative coupling (CDC) of C(sp3)–H/C(sp3)–H bonds to afford olefins by 4H elimination is described. This method employs air (molecular oxygen) as an ideal oxidant, and is performed under mild, ligand-free and base-free conditions. H2O is the only byproduct. Good tolerance of functional groups and high yields have also been achieved. Preliminary mechanistic investigations suggest that the present transformation involves a radical process.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...