Autoxidation: catalyst-free route to silicone rubbers by crosslinking Si–H functional groups†
Abstract
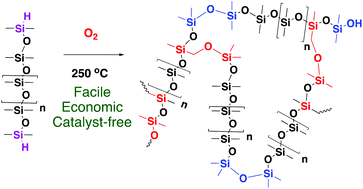
Most traditional methods for silicone elastomer preparation involve catalysts whose incomplete removal can result in compromised thermal stability of the product elastomers and/or safety concerns. Herein, we report the oxidative curing of hydrosilane (H–Si) functionalized polymers to generate silicone elastomers at 250 °C in air but in the absence of catalysts. Both oxygen and Si–H groups are required for the oxidative curing process to occur; standard Me3Si-terminated silicone polymers exhibited no change under the same conditions. There are essentially no restrictions on molecular weights and the nature of Si–H (terminal or pendant) groups exploited in the precursor HSi-containing polymers. The product elastomers are bubble-free, transparent and colorless; they do not exhibit any yellowing after thermal aging at 300 °C in air for 7 days. The moduli can be easily tuned by curing time and [HSi] in the precursors. Chain extension arises from conversion of SiH groups to Si–O–Si linkages, and crosslinks and chain extension are produced via radically induced ether formation (first step: RR′R′′SiH + O2 + MeSi-silicone → RR′R′′SiO-CH2Si-silicone + oxygen species). The efficiency of the radical chain reaction and the resulting crosslinking processes increase with temperature. This process provides a facile, economic, green and catalyst-free way to manufacture silicone elastomers from inexpensive, readily available starting materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...