Enzymatic synthesis of polysaccharide-based copolymers†
Abstract
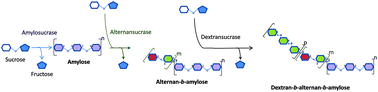
The design of enzymatic routes for the production of biosourced copolymers represents an attractive alternative to chemical synthesis from fossil carbon. In this paper, we explore the potential of glycosynthesizing enzymes to produce novel block copolymers composed of various covalently-linked α-glucans with contrasting structures and physicochemical properties. To this end, various glucansucrases able to synthesize α-glucans with different types of α-osidic bonds from sucrose were tested for their ability to elongate oligosaccharide and polysaccharide acceptors with different structures from the native polymer synthesized by each enzyme. We showed that two enzymes – namely, the alternansucrase from Leuconostoc mesenteroides NRRL B-1355 (specific for α(1 → 6)/α(1 → 3)-linked alternan synthesis) and the dextransucrase DSR-MΔ1 from Leuconostoc citreum NRRL B-1299 (specific for α(1 → 6)-linked dextran formation) – were able to elongate α(1 → 4)-linked amylose and α(1 → 6)/α(1 → 3)-linked alternan respectively. Carrying out stepwise acceptor reactions, and after optimization of the acceptor size and donor/acceptor ratio, two types of diblock copolymers were synthesized – a dextran-b-alternan and an alternan-b-amylose – as well as the triblock copolymer dextran-b-alternan-b-amylose. Their structural characterization, performed by combining chromatographic, NMR and permethylation analyses, showed that the copolymer polymerization degree ranged from 29 to 170, which is the highest degree of polymerization ever reported for an enzymatically synthesized polysaccharide-based copolymer. The addition of dextran and alternan blocks to amylose resulted in conformational modifications and related flexibility changes, as demonstrated by small angle X-ray scattering.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...