Elucidation of the role of betaine hydrochloride in glycerol esterification: towards bio-based ionic building blocks†
Abstract
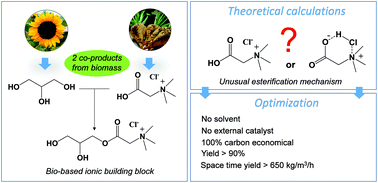
The mechanism of bio-based betaine hydrochloride esterification with glycerol has been studied through DFT modelling and experimental approaches. Interestingly, our proposed mechanism differs from the classical Watson and Ingold ones. In particular, we found that the glycine betaine hydrochloride cluster contains a non-dissociated HCl molecule in its structure. This trapped HCl acted as a proton relay to favor the formation of unconstrained six-membered ring transition state structures both in nucleophilic addition (C–O bond coupling) and H2O elimination pathways. These findings led us to optimize this reaction. In particular, glyceryl betaine esters were produced in a yield up to 90% and with a space time yield up to 670 kg m−3 h−1 unreported to date. The absence of an external catalyst and solvent, as well as the use of a stoichiometric mixture of acidified glycine betaine and glycerol, two co-products of the sugar beet and vegetable oil industries, respectively, represent notable advantages within the framework of sustainable chemistry. This work opens a straightforward route to bio-based and valuable ionic building blocks which are of high interest for the synthesis of ionic surfactants or liquids. Furthermore, the results reported in this work also rationalize the high catalytic performances of glycine betaine hydrochloride recently reported in acid-catalyzed reactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...