Cleavage of a C–C σ bond between two phenyl groups under mild conditions during the construction of Zn(ii) organic frameworks†
Abstract
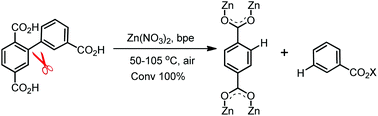
Due to the high bond dissociation energy, low proton acidity, and highly nonpolar character of the C–C bond, activation or cleavage of the bonds, especially the C(sp2)–C(sp2) σ bond, is one of the most challenging tasks in synthetic chemistry. Herein, we present a simple and effective strategy for cleavage of the C(sp2)–C(sp2) σ bond between two phenyl groups under mild reaction conditions during the construction of zinc(II) organic frameworks. By reacting the organic ligand 3-(2′,5′-dicarboxyphenyl)benzoic acid (H3dbba) and 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane (bpe) with Zn(II) ions in dimethylformamide, dimethylacetamide, or diethylformamide solvent systems, complete cleavage of the C(sp2)–C(sp2) σ bonds between two phenyl groups occurred and all H3dbba ligands were broken into 1,4-benzenedicarboxylate (bdc) and benzoic acid, and a new coordination polymer, [Zn(bdc)(bpe)] was obtained. We discuss a plausible mechanism for this cleavage mode and confirm that it occurred. This extraordinary example of C(sp2)–C(sp2) σ bond cleavage under mild conditions provides new insights for both organic and inorganic synthetic chemistry.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...