Hydrolytic degradation of ROMP thermosetting materials catalysed by bio-derived acids and enzymes: from networks to linear materials†
Abstract
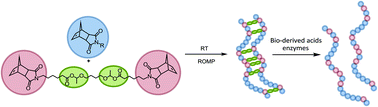
This paper reports the first example of degradable ROMP thermosetting materials catalysed by bio-derived acids and cutinase from Thermobifida cellulosilytica (Thc_Cut1). The ROMP thermosetting materials are based on norbornene dicarboximides containing acetal ester groups only in the crosslinking moiety. The insoluble cross-linked materials were subjected to acid-catalysed hydrolysis using bio-derived acetic and citric acids as well as enzymatic degradation using Thc_Cut1, resulting in the materials becoming completely soluble in dichloromethane. 1H NMR and rheological analysis performed on materials after acid-catalysed hydrolysis showed characteristics indistinguishable to those of the linear polymer analogues. These analyses confirmed the cleavage of the crosslinking moiety upon degradation with the main backbone chains remaining intact. The glass transition temperatures of the polymer materials after acid-catalysed hydrolysis were the same as those observed for the linear polymer analogues. TGA showed that the cross-linked polymers were thermally stable to 150 °C, beyond which they showed weight losses due to the thermal cleavage of the acetal ester linkages.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...