Deoxygenation of carbonyl compounds using an alcohol as an efficient reducing agent catalyzed by oxo-rhenium complexes†
Abstract
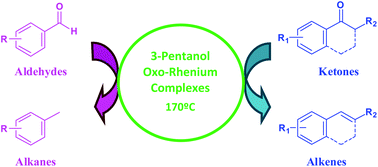
This work describes the first methodology for the deoxygenation of carbonyl compounds using an alcohol as a green solvent/reducing agent catalyzed by oxo-rhenium complexes. The system 3-pentanol/ReOCl3(SMe2)(OPPh3) was successfully employed in the deoxygenation of several aryl ketones to the corresponding alkenes and also in the deoxygenation of aryl aldehydes to alkanes with moderate to excellent yields. The catalyst ReOCl3(SMe2)(OPPh3) can also be used in several catalytic cycles with good activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...