Biotechnological production of acetoin, a bio-based platform chemical, from a lignocellulosic resource by metabolically engineered Enterobacter cloacae†
Abstract
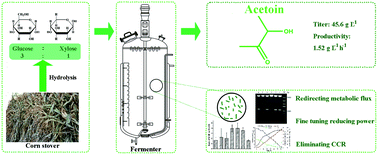
Acetoin (AC) is regarded as one of the top potential sugar-derived chemical building blocks that can be used as food additives, precursors in chemical synthesis, and plant growth promoting molecules. In this study, a low-cost lignocellulosic resource of pretreated corn stover was used as a carbon source to produce AC. After redirecting the metabolic flux, fine tuning reducing power, and eliminating carbon catabolite repression in Enterobacter cloacae SDM, a systematically engineered strain SDM 53 was constructed, which is able to utilize glucose and xylose efficiently and simultaneously. Using fed-batch fermentation of SDM 53, 45.6 g L−1 AC was produced at a rate of 1.52 g L−1 h−1 using the lignocellulosic hydrolysate. Biotechnological synthesis of AC has various advantages such as being sustainable and environment-friendly. With its desirable properties, the engineered strain SDM 53 may be a potential choice for the industrial production of AC.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...