Halogen-free water-stable aluminates as replacement for persistent fluorinated weakly-coordinating anions†
Abstract
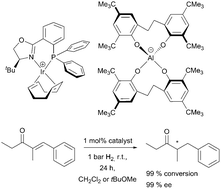
Multigram amounts of halogen-free aluminate salts were prepared from cost-efficient ethylene-bridged bisphenols and alkali aluminium hydrides. The lipophilic, weakly-coordinating “aletbate” anion with eight tert-butyl substituents, the “aletpate” anion with eight tert-pentyl substituents and a formidable solubility reaching from aromatic hydrocarbon solvents to ethanol, and the “alphetbate” anion with four tert-butyl and four 1,1-diphenylethyl substituents, are structurally characterised by highly sterically shielded aluminium(III) centres. The aluminates feature excellent stability towards alcohols, water and aqueous base, and good stability in acidic medium. The sodium aluminates undergo facile salt metathesis reactions in various solvents. Its extraordinary tendency for crystallisation makes aletbate an ideal counterion for salt isolation and purification. Aletpate salts can be highly soluble even in cyclohexene, diethyl ether and toluene. Coordinated tetrahydrofuran can be thermally eliminated from sodium aletbate to yield a reactive sodium(I) adduct that abstracts chloride ligands from transition metal complexes. Iridium(I) aletbate complexes are highly active in the atom-efficient hydrogenation of a,β-unsaturated ketones and aromatic imines at room temperature at an H2 pressure of 1 bar. Thus, the aletbate and aletpate anions can replace halogenated and persistent counterions such as BArF.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...