Dissolution of wood in α-keto acid and aldehydic carboxylic acids and fractionation at room temperature
Abstract
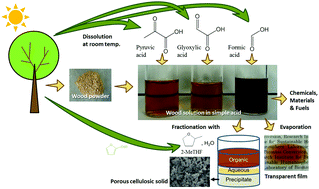
Wood pulverised using a ball mill was dissolved in an α-keto acid, pyruvic acid, and two aldehydic carboxylic acids, namely glyoxylic acid and formic acid, at room temperature. Viscosity and optical transmittance analyses revealed that the wood particles dissolved in glyoxylic acid and formic acid in several hours, while they dissolved in pyruvic acid in several days. Size exclusion chromatography demonstrated that substances with number average molecular mass exceeding 105 were present in every solution. Incubation of these carboxylic acids with methanol produced the corresponding ester and/or (hemi)acetal derivatives, suggesting that the dissolution mechanism involves the substitution of hydroxyl groups in biomass. After dissolution, all solutions demonstrated non-Newtonian fluid behaviour with a non-Newtonian index n ranging from 0.41 to 0.72. When the dissolution time increased, the non-Newtonian index of the formic acid solution increased towards the value for a Newtonian fluid (n = 1). This rise was accompanied by partial depolymerisation. Evaporation of the wood solution gave a smooth transparent film. Using the water-immiscible solvent 2-methyltetrahydrofuran (2-MeTHF), the formic acid solution was separated into cellulosic porous solids, lignin-rich 2-MeTHF-soluble fraction and other components at room temperature. The dissolution of woody biomass at room temperature creates a new biorefinery process for the conversion of wood components in various solution reactions. In particular, in this study, pyruvic acid, which plays a central role in the metabolism of living organisms, is used as a new solvent for wood, thus bridging biochemistry and wood biorefinery.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...