TiO2-photocatalytic acceptorless dehydrogenation coupling of primary alkyl alcohols into acetals†
Abstract
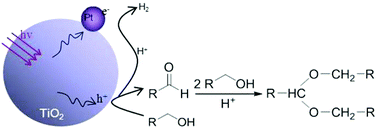
Primary alkyl alcohols can be directly converted into acetals and H2via TiO2-photocatalytic dehydrogenation coupling at room temperature, with no need for any hydrogen acceptors. The reaction follows a tandem process integrating photocatalytic alcohol dehydrogenation and H+-catalytic acetalation, in which the H+ ion catalysts are provided by the alcohol dehydrogenation in real time. This approach exhibits a very high reaction rate and product selectivity, and represents a novel green process for the conversion of primary alkyl alcohols, especially for bio-renewable ethanol and 1-butanol.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...