Formation of uniform colloidal spheres from lignin, a renewable resource recovered from pulping spent liquor†
Abstract
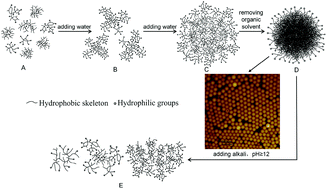
Alkali lignin, recovered from the pulping black liquor, was chemically modified by acetylating, and then used as a biomass resource to prepare uniform colloidal spheres via self-assembly. The self-assembled structure and colloid formation mechanism of the acetylated lignin (ACL) were investigated by DLS, SLS, TEM, AFM, XPS, FTIR, elemental analysis and contact angle measurements. Results show that ACL colloidal spheres are obtained from gradual hydrophobic aggregation of ACL molecules, induced by continuously adding water into the ACL–THF solution. ACL molecules start to form colloidal spheres at a critical water content of 44 vol% when the initial concentration of ACL in THF is 1.0 mg mL−1, and the colloidization process is completed at a water content of 67 vol%. An excessive amount of water is added into the dispersions to “quench” the structures formed and then the ACL dispersion is treated by rotary evaporation for recycling THF and acquiring colloidal spheres. The ACL colloidal spheres have an <Rh> of 110 nm with a polydispersity (μ2/Γ2) of 0.022. The average aggregated number (<Nagg>) in each colloidal sphere and the average density (<ρ>) are estimated to be 1.0 × 105 and 0.187 g cm−3. Preparation of water-dispersive lignin nanoparticles opens up a green and valuable pathway for value-added utilization of lignin biomass recovered from pulping spent liquor, which is of great significance for both the utilization of renewable resources and environmental protection.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...