Further studies on the biodegradation of ionic liquids†
Abstract
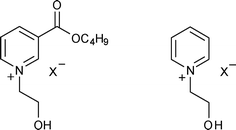
A range of ionic liquids (ILs) containing a pyridinium cation were synthesised and their biodegradability was evaluated using the CO2 headspace test (ISO 14593). ILs bearing a
* Corresponding authors
a
Medicinal Chemistry and Drug Action, Monash Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Monash University, Parkville, Victoria, Australia
E-mail:
peter.scammells@monash.edu
Fax: +61 3 99039582
Tel: +61 3 9903 9542
b
Department of Surfactant Technology, IQAC-CSIC, Jordi Girona 18-26, Spain
E-mail:
mtgbet@iiqab.csic.es
Fax: +34 93 204 5904
Tel: +34 93 400 6100
c
Department of Chemistry, Saint Mary's University, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada
E-mail:
robert.singer@smu.ca
Fax: +1 902 496 8104
Tel: +1 902 496 8189
A range of ionic liquids (ILs) containing a pyridinium cation were synthesised and their biodegradability was evaluated using the CO2 headspace test (ISO 14593). ILs bearing a

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
L. Ford, J. R. Harjani, F. Atefi, M. T. Garcia, R. D. Singer and P. J. Scammells, Green Chem., 2010, 12, 1783 DOI: 10.1039/C0GC00082E
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
