Structure–activity relationship of avocadyne†
Abstract
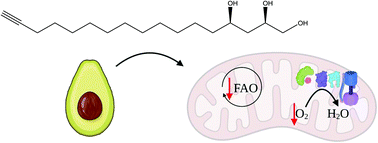
Avocado consumption is associated with numerous health benefits. Avocadyne is a terminally unsaturated, 17-carbon long acetogenin found almost exclusively in avocados with noted anti-leukemia and anti-viral properties. In this study, specific structural features such as the terminal triple bond, odd number of carbons, and stereochemistry are shown to be critical to its ability to suppress mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation and impart selective activity in vitro and in vivo. Together, this is the first study to conduct a structure–activity analysis on avocadyne and outline the chemical moieties critical to fatty acid oxidation suppression.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...