Polysaccharide from Ganoderma lucidum ameliorates cognitive impairment by regulating the inflammation of the brain–liver axis in rats†
Abstract
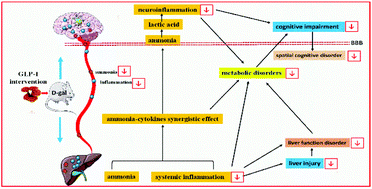
Ganoderma lucidum (G. lucidum) polysaccharide-1 (GLP-1) is one of the polysaccharides isolated from the fruiting bodies of G. lucidum. Inflammation in the brain–liver axis plays a vital role in the progress of cognitive impairment. In this study, the beneficial effect of GLP-1 on D-galactose (D-gal) rats was carried out by regulating the inflammation of the brain–liver axis. A Morris water maze test was used to assess the cognitive ability of D-gal rats. ELISA and/or western blot analysis were used to detect the blood ammonia and inflammatory cytokines levels in the brain–liver axis. Metabolomic analysis was used to evaluate the changes of small molecule metabolomics between the brain and liver. As a result, GLP-1 could obviously ameliorate the cognitive impairment of D-gal rats. The mechanism was related to the decreasing levels of TNF-α, IL-6, phospho-p38MAPK, phospho-p53, and phospho-JNK1 + JNK2 + JNK3, the increasing levels of IL-10 and TGF-β1, and the regulation of the metabolic disorders of the brain–liver axis. Our study suggests that G. lucidum could be exploited as an effective food or health care product to prevent and delay cognitive impairment and improve the quality of life.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...