Isolation and identification of bioactive peptides from Xuanwei ham that rescue oxidative stress damage induced by alcohol in HHL-5 hepatocytes†
Abstract
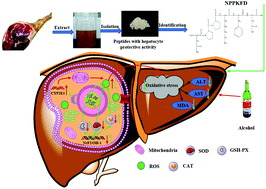
Peptides extracted from Xuanwei ham (XHP) can prevent free radical-induced diseases. The aim of the present study was to isolate and identify bioactive peptides from Xuanwei hams that rescue the oxidative stress damage induced by alcohol in HHL-5 hepatocytes. Alcohol-treated HHL-5 human hepatocytes were utilized as the alcohol-induced hepatocyte damage model to evaluate the effects of XHP on amounts of aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and malondialdehyde (MDA). The result showed that XHP could significantly reduce ALT, AST and MDA, the major biomarkers of liver damage. The crude XHP was separated by size exclusion chromatography, followed by the evaluation of respective activities. Then, the most active components were further separated by RP-HPLC, and their activities were evaluated according to the above method. The peptide was identified as a hexapeptide with the sequence of Asn-Pro-Pro-Lys-Phe-Asp (NPPKFD) through LC-MS/MS. Further, the molecular mechanisms by which NPPKFD prevents alcohol-induced oxidative stress damage were revealed. Results showed that the hexapeptide could downregulate CYP2E1 expression, reduce generation of ROS and enhance oxidant defense systems via the activation of NrF2/HO-1 pathway. The findings suggest that Xuanwei ham can be used as a new source of bioactive peptides for protection from alcohol-induced liver damage.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...