Phytochemicals as modifiers of gut microbial communities
Abstract
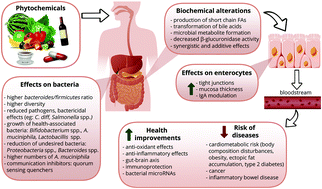
A healthy gut microbiota (GM) is paramount for a healthy lifestyle. Alterations of the GM have been involved in the aetiology of several chronic diseases, including obesity and type 2 diabetes, as well as cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. In pathological conditions, the diversity of the GM is commonly reduced or altered, often toward an increased Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio. The colonic fermentation of dietary fiber has shown to stimulate the fraction of bacteria purported to have beneficial health effects, acting as prebiotics, and to increase the production of short chain fatty acids, e.g. propionate and butyrate, while also improving gut epithelium integrity such as tight junction functionality. However, a variety of phytochemicals, often associated with dietary fiber, have also been proposed to modulate the GM. Many phytochemicals possess antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that may positively affect the GM, including polyphenols, carotenoids, phytosterols/phytostanols, lignans, alkaloids, glucosinolates and terpenes. Some polyphenols may act as prebiotics, while carotenoids have been shown to alter immunoglobulin A expression, an important factor for bacteria colonization. Other phytochemicals may interact with the mucosa, another important factor for colonization, and prevent its degradation. Certain polyphenols have shown to influence bacterial communication, interacting with quorum sensing. Finally, phytochemicals can be metabolized in the gut into bioactive constituents, e.g. equol from daidzein and enterolactone from secoisolariciresinol, while bacteria can use glycosides for energy. In this review, we strive to highlight the potential interactions between prominent phytochemicals and health benefits related to the GM, emphasizing their potential as adjuvant strategies for GM-related diseases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...