Neuroprotective effects of oolong tea extracts against glutamate-induced toxicity in cultured neuronal cells and β-amyloid-induced toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans†
Abstract
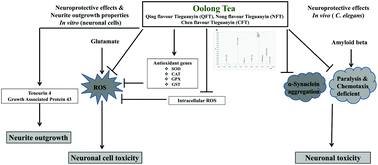
Oolong tea, a traditional Chinese tea, is especially popular in south China and has a variety of health benefits. However, studies about its neuroprotective and neuroregenerative properties are still limited. This study explored the neuroprotective and neurite outgrowth-promoting properties of oolong tea in cultured neuronal cells (Neuro-2a and HT22) and Caenorhabditis elegans models. Ultra performance liquid chromatography was applied to identify the main natural bioactive compounds in oolong tea. Using Neuro-2a and HT22 cells, we found that oolong tea extracts had a protective effect against glutamate-induced cell death. The extracts reduced intracellular reactive oxygen species accumulation and induced gene expression of cellular antioxidant enzymes such as GPx, GSTs and SODs. These extracts also increased the average neurite length, and GAP-43 and Ten-4 mRNA expression in Neuro-2a cells. Moreover, they had protective effects against Aβ-induced paralysis, chemotaxis deficiency and α-synuclein aggregation in C. elegans. This is the first study showing the neuroregenerative and neuroprotective potential of the oolong tea extracts against glutamate/Aβ/α-synuclein-induced toxicity in vitro and in vivo. Our study may support oolong tea extracts as potential candidates for the prevention of neurodegenerative diseases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...