Antimicrobial activity and mechanism of peptide CM4 against Pseudomonas aeruginosa†
Abstract
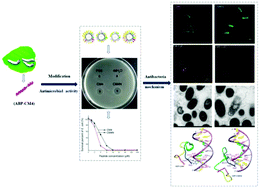
Antibacterial peptide CM4 (ABP-CM4) is a small cationic peptide with broad-spectrum activities against bacteria, fungi and tumor cells and may possibly be used as an antimicrobial agent. In this study, a C-terminal amidated antibacterial peptide ABP-CM4 (ABP-CM4N) with the strongest antibacterial activity was obtained through screening the antibacterial activities of ABP-CM4 with different modifications. The minimal inhibitory concentration of ABP-CM4N was 8 μM against P. aeruginosa (ATCC 27853) which was lower than that of ABP-CM4 (16 μM). The strengthened antimicrobial activity of ABP-CM4N may be associated with the increased membrane binding capacity, being two times that of ABP-CM4 (p < 0.001). The antibacterial mechanism of ABP-CM4N to Pseudomonas aeruginosa was examined by means of cell membrane integrity analysiss, the intracellular ultrastructure change observation and E. coli genomic DNA binding assay. It was found that ABP-CM4N had the same antimicrobial mechanism as ABP-CM4, and the aim of the antimicrobial mechanism was mainly to destroy the cell membrane which caused nucleic acid or protein leakage, and secondly to interact with E. coli genomic DNA after penetrating the cell membrane. Furthermore, in vitro ABP-CM4N showed a better bacteriostatic activity in meats, with the treated samples showing two to three times less positive colonies than ABP-CM4.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...