Antibacterial potential of a novel Lactobacillus casei strain isolated from Chinese northeast sauerkraut and the antibiofilm activity of its exopolysaccharides
Abstract
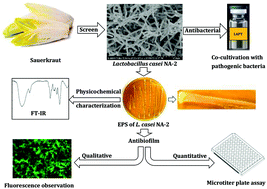
Lactobacillus spp., as probiotics, have shown efficacy in the inhibition of pathogenic bacteria in the intestinal tract. In this study, we investigated the antibacterial activity of Lactobacillus casei NA-2, which was isolated from northeast sauerkraut in China. The results of co-culture suggested that L. casei NA-2 could inhibit the growth of Bacillus cereus, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli O157:H7. Moreover, L. casei NA-2 could adhere to the four pathogenic bacteria potentially associated with its exopolysaccharide (EPS). EPS from L. casei NA-2 was then isolated and its activity determined. The results showed that EPS inhibited the biofilms of B. cereus, S. aureus, S. typhimurium and E. coli O157:H7, with the highest inhibition ratios of 95.5% ± 0.1%, 30.2% ± 3.3%, 14.3% ± 0.6%, and 16.9% ± 5.4%, respectively. Moreover, EPS was able to disperse B. cereus, S. aureus, S. typhimurium and E. coli O157:H7 by 94.1% ± 1.2%, 31.8% ± 8.6%, 40.8% ± 3.3% and 49.6% ± 3.8%, respectively. Results showed that EPS from L. casei NA-2 have potential antibacterial properties by inhibiting biofilm formation and dispersing pathogenic bacteria. In conclusion, the antibiofilm property of the EPS on the surface of L. casei NA-2 is one of the possible reasons for antibacterial activity of L. casei NA-2.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...