Evaluation of Tenebrio molitor protein as a source of peptides for modulating physiological processes†
Abstract
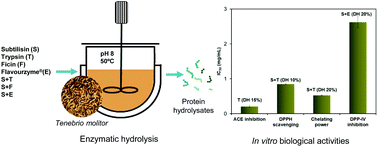
The increasing world population has led to the need to search for new protein sources, such as insects, the harvesting of which can be economical and environmentally sustainable. This study explores the biological activities (angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibition, antioxidant capacity, and dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibition) of Tenebrio molitor hydrolysates produced by a set of food-grade proteases, namely subtilisin, trypsin, ficin and flavourzyme, and the degree of hydrolysis (DH), ranging from 5% to 20%. Trypsin hydrolysates exhibited the highest ACE inhibitory activity at a DH of 10% (IC50 0.27 mg mL−1) in the experimental series, which was attributed to the release of short peptides containing Arg or Lys residues in the C terminus, and described as the ACE-inhibition feature. The levels of in vitro antioxidant activities were comparable to those reported for insect species. Subtilisin and trypsin hydrolysates at a DH of 10% displayed optimal DPPH scavenging and ferric reducing activities, which was attributed to the presence of 5–10-residue active peptides, as reported in the literature. Iron chelating activity was significantly favoured by increasing the DH, attaining a minimal IC50 of 0.8 mg mL−1 at a DH of 20% regardless of the enzymatic treatment. Similarly, in vitro antidiabetic activity was significantly improved by extensive hydrolysis, and, more specifically, the presence of di- and tripeptides. In this regard, the combined treatment of subtilisin–flavourzyme at a DH of 20% showed maximal DPP-IV inhibition (IC50 2.62 mg mL−1). To our knowledge, this is the first study evaluating the DPP-IV activity of Tenebrio molitor hydrolysates obtained from these commercial proteases. We conclude that Tenebrio molitor hydrolysates produced with food-grade proteases are a valuable source of active peptides that can be used as functional ingredients in food and nutraceutical preparations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...