Chrysanthemum ethanol extract induced loss of Kupffer cells via the mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathway†
Abstract
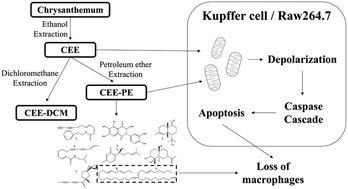
Chrysanthemum has been viewed as an important traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) with a long history. Research studies indicated many potential pharmaceutical effects of chrysanthemum extract. However, hardly any investigation has been performed to describe its toxicity. In this study, acute application of chrysanthemum ethanol extract (CEE, 300 mg kg−1) was found to induce apoptosis of hepatic Kupffer cells in vivo. CEE was also observed to induce apoptosis of RAW264.7 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Further analysis using flow cytometry and western blotting revealed that CEE induced apoptosis of RAW264.7 cells via a mitochondria-dependent pathway. After a HPLC combined screening assay, we narrowed down the toxicity caused by the petroleum extract of CEE (CEE-PE, 66 μg mL−1). In vivo effects of CEE-PE were also tested in mice. Additionally, nine potential toxic compounds were isolated and identified from CEE-PE. In all, we found that components with small polarities in CEE could induce apoptosis of Kupffer cells and macrophages via a mitochondrial dependent pathway, which might draw attention to the safety issues of everyday use of chrysanthemum.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...