Synbiotic supplementation containing Bifidobacterium infantis and xylooligosaccharides alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis†
Abstract
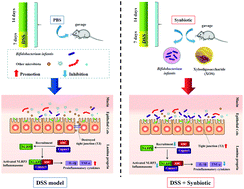
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease whose prevalence is increasing globally. A synbiotic has probiotic and prebiotic components and is regarded as a promising candidate for alleviating UC-associated inflammation. The purpose of this study is to determine whether there is an additive efficacy between the probiotic Bifidobacterium infantis (B. infantis) and the prebiotic xylooligosaccharide (XOS) against UC. C57BL/6 mice were treated with B. infantis, XOS, or synbiotic (combination of B. infantis and XOS) for 21 d. During the final 7 d of treatment, the mice were administered dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) dissolved in drinking water to induce colitis. All treatments decreased the disease activity index (DAI) and pathological scores, and synbiotic treatment was more efficacious than either the probiotic or prebiotic alone. Compared with the DSS-induced colitis group, all treatment groups significantly downregulated the proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β, and synbiotic treatment significantly upregulated the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 in the colon tissues. Furthermore, all treatments significantly reduced the NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome mRNA level in the colon tissues. All treatments significantly inhibited oxidative stress and increased zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1), occludin, and claudin-1 tight junction (TJ) molecule mRNA levels in the colon tissues. Therefore, the observed efficacy of synbiotics against colitis may be explained by the additive combination of the direct anti-inflammatory effects of the probiotic and prebiotic components and their ability to fortify colonic epithelial barrier integrity. Our findings suggest that a synbiotic is a promising dietary supplement or functional food for the effective management of UC.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Food & Function Recent HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...