A lupine (Lupinus angustifolious L.) peptide prevents non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in high-fat-diet-induced obese mice†
Abstract
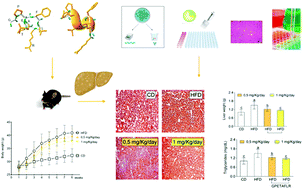
Bioactive peptides are related to the prevention and treatment of many diseases. GPETAFLR is an octapeptide that has been isolated from lupine (Lupinus angustifolius L.) and shows anti-inflammatory properties. The aim of this study was to evaluate the potential activity of GPETAFLR to prevent non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in high-fat-diet (HFD)-induced obese mice. C57BL/6J mice were fed a standard diet or HFD. Two of the groups fed the HFD diet were treated with GPETAFLR in drinking water at 0.5 mg kg−1 day−1 or 1 mg kg−1 day−1. To determine the ability of GPETAFLR to improve the onset and progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, histological studies, hepatic enzyme profiles, inflammatory cytokine and lipid metabolism-related genes and proteins were analysed. Our results suggested that HFD-induced inflammatory metabolic disorders were alleviated by treatment with GPETAFLR. In conclusion, dietary lupine consumption can repair HFD-induced hepatic damage possibly via modifications of liver's lipid signalling pathways.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Food & Function Recent HOT articles and Food & Function Recent Open Access Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...