Camellia oil (Camellia oleifera Abel.) attenuates CCl4-induced liver fibrosis via suppressing hepatocyte apoptosis in mice
Abstract
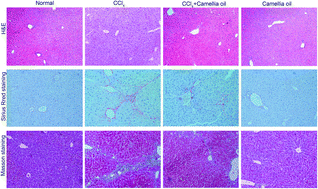
Liver fibrosis is a common part of the pathological development of many chronic liver diseases. As liver fibrosis progresses, it may lead to cirrhosis, portal hypertension, liver decompensation, liver tumours, and death. Camellia oil (Camellia oleifera Abel.) is widely used as an edible oil in China. It has a wide range of biological activities and is used as a traditional medicine to treat conditions such as burns and stomach pains. However, whether camellia oil can ameliorate liver fibrosis remains unclear. We constructed a liver fibrosis model induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and then confirmed the role of camellia oil in liver fibrosis by biochemical examination, histopathological morphology, immunohistochemistry, and western blot analysis. We found that camellia oil ameliorated histopathological lesions, improved liver function and antioxidant capacity, decreased the expression of TGF-β1 and α-SMA proteins, and downregulated the expression of the pro-apoptotic proteins in CCl4-induced liver fibrosis. Therefore, these results suggest that camellia oil attenuates CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice, and its mechanism may function via reduction of hepatocyte apoptosis to inhibit hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation. Camellia oil may provide a potential new treatment for liver fibrosis as an auxiliary treatment by addition of the edible oil to the daily diet.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...