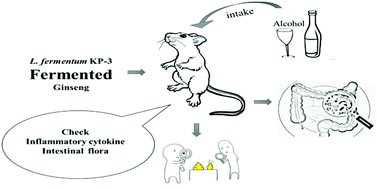
Fermented ginseng improved alcohol liver injury in association with changes in the gut microbiota of mice
Abstract
The interactions among the liver, intestine and immune system play an important role in alcoholic liver injury. In this study, C57BL/6N mice with alcoholic injury were treated with unfermented and Lactobacillus fermentum KP-3-fermented ginseng. The indicators of hepatic steatosis, inflammation and injury were evaluated. The number of beneficial and harmful bacteria in the mice ileum and colon was counted by a traditional method; moreover, the diversity analysis of the cecum flora was performed. The alcohol exposure increased the levels of ALT, AST, TNF-α and IL-6 inflammatory factors and liver steatosis. In addition, the alcohol-fed miceexhibited a lower number of Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria in the ileum and colon; the cecum flora diversity in the mice showed that alcohol obviously enhanced the abundance of the unclassified S24-7 of the Bacteroidetes phylum and the Proteobacteria genus of the Sutterella phylum and reduced the abundance of short-chain fatty acid-producing bacteria such as Akkermansia in the Verrucomicrobia phylum and those belonging to the Allobaculum genus, the Ruminococcus genus, and the Adlercreutzia genus in the Actinobacteria phylum. All these changes were improved by fermented ginseng. Conclusively, fermented ginseng could alleviate the alcoholic liver injury and disorder of the intestine by adjusting the intestinal flora.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...