High-fat diet induces mouse liver steatosis with a concomitant decline in energy metabolism: attenuation by eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) or hydroxytyrosol (HT) supplementation and the additive effects upon EPA and HT co-administration†
Abstract
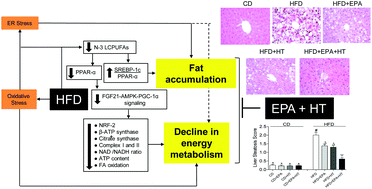
High-fat-diet (HFD) feeding is associated with liver oxidative stress (OS), n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid (n-3 LCPUFA) depletion, hepatic steatosis and mitochondrial dysfunction. Our hypothesis is that the HFD-induced liver injury can be attenuated by the combined supplementation of n-3 LCPUFA eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and the antioxidant hydroxytyrosol (HT). The C57BL/6J mice were administered an HFD (60% fat, 20% protein, 20% carbohydrates) or control diet (CD; 10% fat, 20% protein, 70% carbohydrates), with or without EPA (50 mg kg−1 day−1), HT (5 mg kg−1 day−1), or EPA + HT (50 and 5 mg kg−1 day−1, respectively) for 12 weeks. We measured the body and liver weights and dietary and energy intakes along with liver histology, FA composition, steatosis score and associated transcription factors, mitochondrial functions and metabolic factors related to energy sensing through the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and PPAR-γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α) cascade. It was found that the HFD significantly induced liver steatosis, with a 66% depletion of n-3 LCPUFAs and a 100% increase in n-6/n-3 LCPUFA ratio as compared to the case of CD (p < 0.05). These changes were concomitant with (i) a 95% higher lipogenic and 70% lower FA oxidation signaling, (ii) a 40% diminution in mitochondrial respiratory capacity and (iii) a 56% lower ATP content. HFD-induced liver steatosis was also associated with (iv) a depressed mRNA expression of AMPK-PGC-1α signaling components, nuclear respiratory factor-2 (NRF-2) and β-ATP synthase. These HFD effects were significantly attenuated by the combined EPA + HT supplementation in an additive manner. These results suggested that EPA and HT co-administration partly prevented HFD-induced liver steatosis, thus strengthening the importance of combined interventions in hepatoprotection in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Celebrating Latin American Talent in Chemistry

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...