Salvianolic acid B (Sal B) alleviates the decreased activity induced by prednisolone acetate on osteoblasts by up-regulation of bone formation and differentiation genes†
Abstract
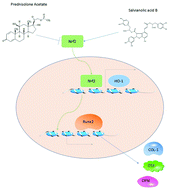
Glucocorticoids (GCs) are widely used to treat a variety of autoimmune diseases, but long-term use can lead to osteoporosis. To elucidate the mechanism of osteoporosis caused by glucocorticoids and to find effective protective drugs/foods, osteoblasts treated by prednisolone acetate were studied and salvianolic acid B (Sal B) was added to osteoblasts. The results showed that Sal B increased the activity of ALP and stimulated the expression of ALP that had been suppressed by prednisolone acetate. To further study the mechanisms of the protective effect of Sal B on osteoblasts treated with prednisolone acetate, the effects of gene expression involved with bone formation and differentiation were studied. The results show that the mRNA and protein expression of Runx2, Osx, OCN, IGF-I, Col-I and HO-I was up-regulated by Sal B. In conclusion, by stimulating the osteoblast activity and the expression of genes related to bone formation and differentiation, Sal B had a protective effect on osteoblasts that had been treated with prednisolone acetate.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...