S-Petasin isolated from Petasites japonicus exerts anti-adipogenic activity in the 3T3-L1 cell line by inhibiting PPAR-γ pathway signaling†
Abstract
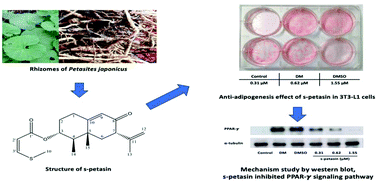
Petasites japonicus is an edible and medicinal plant with a good flavor, and it is a rich source of bioactive compounds. S-Petasin has been isolated from Petasites hybridus (L.), Petasites officinalis (L.) and Petasites formosanus, but not from Petasites japonicus. In this study, we found that hexane extracts of Petasites japonicus inhibited adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. After this we isolated s-petasin from Petasites japonicus. Subsequently, the 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes were used to test whether s-petasin exerts an anti-adipogenic effect. The results showed that s-petasin presented strong anti-adipogenic activity. Further studies illustrated that s-petasin reduced glucose uptake. Moreover, results showed that triglyceride accumulation was inhibited by s-petasin in differentiated 3T3-L1 cells. Western blot assay indicated that s-petasin down-regulated the expression of PPAR-γ and its target genes in a dose dependent manner. In conclusion, we isolated s-petasin from Petasites japonicus and found that it exerted anti-adipogenic activity against 3T3-L1 cell differentiation through inhibition of the expression of PPAR-γ pathway signaling.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...