A holistic view of gallic acid-induced attenuation in colitis based on microbiome-metabolomics analysis†
Abstract
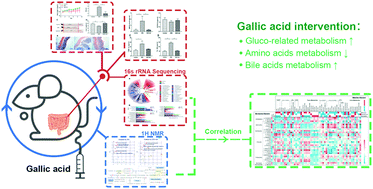
Gallic acid (GA), a plant phenol found in fruits and vegetables, has been recently reported to attenuate ulcerative colitis (UC). However, the mechanism of GA in UC remains unknown. In this study, we investigated the therapeutic effects of GA on UC from the perspective of gut microbiota and supervised the metabolic alterations in vivo with 1H NMR-based metabolomics, which can provide a holistic view to understand the functions of GA in UC. Rats with dextra sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis were rectally administrated with GA (6 mg kg−1) for 8 consecutive days. 16S gene sequencing was performed on feces samples to obtain bacterial community information. Urine and feces samples were analyzed with 1H NMR spectroscopy, and short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) in feces and colon contents were detected with gas chromatography. Our results showed that UC syndromes in the GA group were significantly attenuated. The microbial alterations in the DSS group were characterized by a decrease of probiotic bacteria, such as Lactobacillaceae and Prevotellaceae, and an increase of some pathogenic species, mainly in the Firmicutes and Proteobacteria phyla. GA treatment could modulate the microbiota composition towards a similar proportion to the control group. Metabolic data further revealed that the GA-induced metabolic changes focus on increasing carbohydrate metabolism (gluco-related metabolism) and bile acid (BA) metabolism and decreasing amino acid metabolism, which also provides evidence for alteration of the microbiota because these feces metabolites are by-products of interactions between the host and the microbiota. These findings demonstrate GA-induced alterations in metabolic and bacterial profiles in DSS-colitis, providing new insight into the attenuation of GA in UC.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...