Donkey milk oligosaccharides influence the growth-related characteristics of intestinal cells and induce G2/M growth arrest via the p38 pathway in HT-29 cells†
Abstract
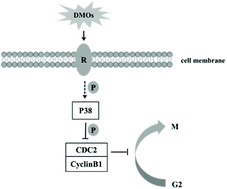
Donkey milk is considered to be a valuable nutritional source. Deeper knowledge of the constituents of donkey milk is necessary. As multifunctional components of milk, oligosaccharides have been reported to have the potential to support intestine development. We studied the composition and content of donkey milk oligosaccharides (DMOs). Sialylated oligosaccharides were found to be the primary oligosaccharides in DMOs, consisting of 3′-sialyllactose (SL) and 6′-SL. The amount of 3′-SL and 6′-SL in donkey milk was 18.3 ± 0.7 mg L−1 and 33.1 ± 0.7 mg L−1, respectively. Moreover, we found that DMOs induced differentiation, promoted apoptosis and inhibited proliferation in HT-29, Caco-2 and HIEC cells in a concentration-dependent manner, suggesting that DMOs promote maturation of intestinal epithelial cells. The mechanism of the DMOs’ effects on HT-29 cells was associated with activation of the p38 pathway and cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase. Our research will help understand the biological functions of DMOs and assess their potential roles in infant nutrition.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...