Evaluation of the anti-inflammatory properties of the active constituents in Ginkgo biloba for the treatment of pulmonary diseases
Abstract
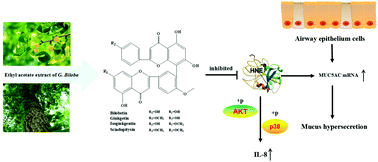
Ginkgo biloba has long been used in ancient China for the treatment of cough, asthma, and other lung diseases. However, the active constituents in G. biloba for pulmonary disease treatment remain unclear. The objective of this study was to evaluate the anti-inflammatory active constituents in G. biloba and clarify their associated molecular mechanisms. The biological effects of different G. biloba extracts were evaluated in an ovalbumin-induced allergic mouse model. Anti-inflammatory compounds were present in the ethyl acetate phase of the extract, which were analysed by HPLC-MS. Biflavones were identified as the main compounds, which were further evaluated by docking calculations. Leukocyte elastase showed a high fit score with ginkgetin, one of the identified biflavones. The lowest binding free energy was −6.69 kcal mol−1. The effects of biflavones were investigated in vivo and in vitro. Ginkgetin markedly suppressed the abnormal expression of the Akt and p38 pathways in human neutrophil elastase (HNE)-stimulated A549 cells. Biflavones also decreased MUC5AC mRNA expression in HNE-stimulated A549 cells and the allergic mouse model. Inflammatory cells (neutrophils) and cytokines (IL-8) also decreased in mice treated with biflavones. The results suggest that G. biloba biflavones could inhibit the activity of leukocyte elastase. This in turn implicates G. biloba as a functional food for the treatment of airway inflammation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...