Understanding the role of extracts from sea buckthorn seed residues in anti-melanogenesis properties on B16F10 melanoma cells†
Abstract
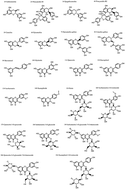
The hydroalcoholic extract of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) seed residues (HYD-SBSR) is a potential skin whitening agent. To test this material as a potential skin whitening agent, we identified and quantified the main chemical constituents of HYD-SBSR by using ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadruple time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS) and ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with triple quadruple mass spectrometry (UPLC-QQQ-MS). The anti-melanogenesis properties of HYD-SBSR on B16F10 mouse melanoma cells were analysed and the mechanism was measured on both the transcriptional and translational levels. About 24 compounds were identified. Kaempferol and its derivatives were the main compounds with a concentration of about (2796.22 ± 31.55) μg per g DW. The following order among the detected compounds was observed: quercetin and its derivatives > isorhamnetin and its derivatives > procyanidins. HYD-SBSR has a strong antioxidant activity but with a slight cytotoxic effect on B16F10 when treated with 45.45 μg mL−1 and 4.55 μg mL−1 respectively, for 48 h. HYD-SBSR has been found to significantly decrease melanin content (P < 0.01) in 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h. Additionally, strong inhibitory extracellular tyrosinase activities and decreasing intracellular tyrosinase activities were also observed (P < 0.01). HYD-SBSR shows inhibitory effects on the expression of tyrosinase (TYR) and tyrosinase-related protein 1 (TRP-1), and the secretion of TYR and TRP-1 proteins in cell lines. The protein levels of tyrosinase-related protein 2 (TRP-2) and microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) showed no significant difference. HYD-SBSR may inhibit melanin synthesis by decreasing the tyrosinase activity and down-regulating the expression of TYR and TRP-1 which were probably induced by other transcriptional factors rather than MITF.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...