Metabolic and genetic response to probiotics supplementation in patients with diabetic nephropathy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial†
Abstract
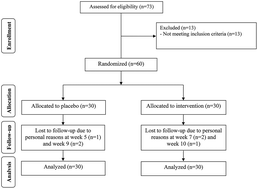
This study was carried out to evaluate the effects of probiotics administration on the metabolic and genetic profiles in patients with diabetic nephropathy (DN). This was a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial with homeostasis model of assessment-estimated insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) as the primary and other metabolic profiles, and biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress as the secondary outcomes. This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial was performed on 60 patients with DN. The patients were randomly assigned into two groups to receive either 8 × 109 CFU day−1 probiotic supplements or placebo (n = 30 in each group) for 12 weeks. Fasting blood was collected at the baseline and end of intervention to measure glycemic control, lipid profiles, biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress. Multiple linear regression models were used to assess the treatment effects on the outcomes adjusting for confounding variables. Probiotics supplementation, compared with the placebo, resulted in a significant reduction in fasting plasma glucose (P = 0.01), serum insulin concentrations (P = 0.01) and HOMA-IR (P = 0.007), and a significant increase in the quantitative insulin sensitivity check index (P = 0.04). Additionally, compared with the placebo, probiotic intake resulted in a significant reduction in triglycerides (P = 0.001) and total-/HDL-cholesterol ratio (P < 0.001), and a significant increase in HDL-cholesterol levels (P < 0.001). Supplementation with probiotics, compared with the placebo, was associated with a significant reduction in high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (P = 0.001), malondialdehyde (P < 0.001) and advanced glycation end products (P < 0.001), and a significant elevation in plasma total glutathione (P < 0.001). Overall, our study indicated that probiotics supplementation had beneficial effects on glycemic control and markers of cardio-metabolic risk.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...