Major compounds of red ginseng oil attenuate Aβ25–35-induced neuronal apoptosis and inflammation by modulating MAPK/NF-κB pathway
Abstract
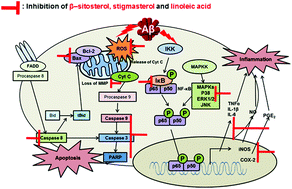
β-Amyloid (Aβ)-induced neuronal toxicity in Alzheimer's disease (AD) is associated with complex mechanisms. Thus, a multi-target approach might be suitable for AD treatment. Following our previous study on the neuroprotective effects of red ginseng oil extract, its major compounds, including linoleic acid (LA), β-sitosterol (BS), and stigmasterol (SS), were examined to elucidate the mechanism of anti-apoptosis and anti-inflammation in Aβ25–35-stimulated PC12 cells. The results showed that the three compounds mitigated Aβ25–35 toxicity by regulating oxidative stress, apoptotic responses, and pro-inflammatory mediators. LA and SS strongly regulated intrinsic apoptosis markers, such as mitochondrial membrane potential, intracellular Ca2+, Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, and caspases-9, -3, and -8. However, BS blocked only the intrinsic apoptotic pathway, particularly by suppressing Ca2+ accumulation. Furthermore, all three compounds downregulated iNOS and phospho-nuclear factor-κB, but only LA and SS inhibited the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and phospho-IκB. In assays to evaluate MAPK expression for confirming upstream signal pathways, BS decreased the phosphorylation of p38 and ERK, but not JNK, while SS markedly decreased the phosphorylation of all three MAPKs, and LA clearly decreased the phosphorylation of ERK and JNK, but not p38. These results indicate that LA, BS, and SS act as neuroprotectives against Aβ25–35-induced injury by distinct molecular mechanisms, indicating their preventive and/or therapeutic potential to treat AD.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...