Anti-inflammatory effect of xanthomicrol, a major colonic metabolite of 5-demethyltangeretin
Abstract
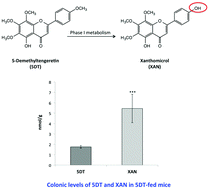
5-Demethyltengeretin (5DT) is a citrus flavonoid with various potential health benefits. To provide physiologically relevant information on the anti-inflammatory properties of 5DT, we identified the major metabolite of 5DT in the mouse colon and established its anti-inflammatory effects in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. CD-1 mice were fed with a 5DT-containing diet for four weeks, and colonic mucosa samples were collected and subjected to LC-MS analysis. Xanthomicrol (XAN) was identified as the major metabolite of 5DT in the mouse colon. More importantly, the colonic level of XAN was about 3.1-fold higher than that of 5DT. The anti-inflammatory effects of 5DT and XAN were determined in LPS-stimulated macrophages. XAN produced significant inhibitory effects on the production of nitric oxide and PGE2. Western blotting and real-time PCR analyses demonstrated that XAN greatly decreased the protein and mRNA levels of iNOS as well as the protein level of COX-2. Furthermore, XAN also reduced the production of pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1β and induced the expression of anti-oxidative enzyme HO-1. Conclusion: Our results demonstrated that XAN is a major metabolite of 5DT in the colon of mice fed with 5DT, and XAN may play important roles in the anti-inflammatory effects elicited by orally administered 5DT.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
