A comparative study of eicosapentaenoic acid enriched phosphatidylcholine and ethyl ester in improving cognitive deficiency in Alzheimer's disease model rats
Abstract
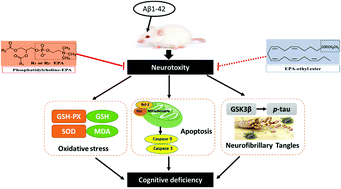
Abundant studies have highlighted the protective effects of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), in the form of glycerolipids (glycerophosphatides and triglycerides) and DHA-ethyl esters (DHA-EE) in Alzheimer's disease (AD); however, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) has rarely been implicated. In the present study, we compared the effects of dietary EPA in the form of phosphatidylcholine (EPA-PC) and EE with DHA-EE (DHA/EPA = 60 mg kg−1 d−1, i.g., 20 days) on cognitive deficits in AD rats. EPA-PC, rather than EPA-EE, significantly improved Aβ-induced cognitive impairment and has a comparable effect with DHA-EE. Further research indicated that EPA-PC and DHA-EE could significantly decrease lipid peroxidation levels, alleviate mitochondria-dependent apoptosis, and inhibit the hyperphosphorylation of tau mediated by GSK3β. These findings suggest that EPA in the form of phosphatidylcholine rather than an ethyl ester has a comparable effect with DHA in improving cognitive impairment in Aβ1–42-induced AD rats.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...