Milk-derived bioactive peptides protect against oxidative stress in a Caco-2 cell model†
Abstract
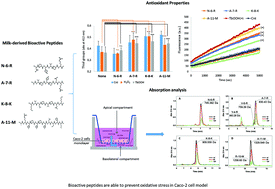
Milk and milk-derived products are a relevant source of bioactive peptides, which are also potential components of functional foods. Bioactive peptides exert multiple actions including an antioxidant role. In the present paper, four synthetic peptides (NPYVPR, AVPYPQR, KVLPVPEK, and ARHPHPHLSFM), corresponding to milk-derived peptides were studied. Although with different features, as revealed by RP-HPLC chromatography and MS analysis, the obtained peptides were shown to be taken up by Caco-2 cells arranged in an epithelial monolayer formation. The four peptides were all able to preserve cell viability against induced oxidative stress indicating that they might have a role in the control of oxidative stress. Therefore, an estimation of total thiols and glutathione content was performed after cell treatment with oxidants like hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) or tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TbOOH). The peptides were able to prevent the decrease of both total thiols and glutathione induced by H2O2 or TbOOH, and, in addition, they showed a protective effect on the thiol-related antioxidant enzymes thioredoxin reductase and glutathione reductase. Finally, they caused a decrease of ROS production induced by TbOOH in Caco-2 cells. The reported results highlight the relevant antioxidant role played by bioactive peptides in cells, which adds to other previously known properties.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Around the Supermarket: Staple Foods


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...