Apigenin exhibits protective effects in a mouse model of d-galactose-induced aging via activating the Nrf2 pathway
Abstract
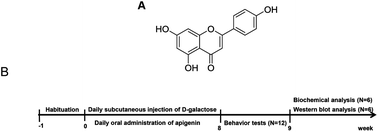
The aim of the present research was to study the protective effects and underlying mechanisms of apigenin on D-galactose-induced aging mice. Firstly, apigenin exhibited a potent antioxidant activity in vitro. Secondly, D-galactose was administered by subcutaneous injection once daily for 8 weeks to establish an aging mouse model to investigate the protective effect of apigenin. We found that apigenin supplementation significantly ameliorated aging-related changes such as behavioral impairment, decreased organic index, histopathological injury, increased senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SAβ-gal) activity and advanced glycation end product (AGE) level. Further data showed that apigenin facilitated Nrf2 nuclear translocation both in aging mice and normal young mice, and the Nrf2 expression of normal young mice was higher than that of natural senile mice. In addition, the expressions of Nrf2 downstream gene targets, including HO-1 and NQO1, were also promoted by apigenin administration. Moreover, apigenin also decreased the MDA level and elevated SOD and CAT activities. In conclusion, focusing on the Nrf2 pathway is a suitable strategy to delay the aging process, and apigenin may exert an anti-senescent effect process via activating the Nrf2 pathway.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...