Molecular mechanisms of the effects of the ethanolic extract of Muntingia calabura Linn. fruit on lipopolysaccharide-induced pro-inflammatory mediators in macrophages
Abstract
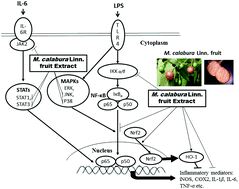
Four flavonoids (epicatechin, rutin, diosmin and luteolin) and 11 phenolic acids (gallic acid, gentisic acid, p-hydroxybezoic acid, vanillic acid, caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, ferulic acid, sinapic acid, syringic acid, p-anisic acid and rosmarinic acid) were determined in the ethanolic extract of M. calabura Linn. fruit gathered in Taiwan. The extract suppressed the lipopolysaccharide-stimulated expressions of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 as well as the productions of nitric oxide, prostaglandin E2 and pro-inflammatory cytokines [tumour necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6] in RAW264.7 macrophages. The extract modulated the inflammatory processes through inactivation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) p38 and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase 1/2 (JNK1/2), and Janus kinase 2 (JAK2)/signal transducers and activators of transcription 1/3 (STAT1/3). Moreover, the activation of nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) followed by inducing the production of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) is also related to the anti-inflammatory effect of the extract.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...