Proanthocyanidins purified from fruit pericarp of Clausena lansium (Lour.) Skeels as efficient tyrosinase inhibitors: structure evaluation, inhibitory activity and molecular mechanism
Abstract
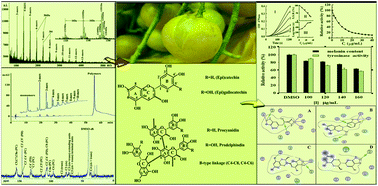
Fruit pericarp of Clausena lansium (Lour.) Skeels, a food waste, was selected as a raw material for proanthocyanidins. The proanthocyanidins’ structures were integrally analyzed using three methods: matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS), high performance liquid chromatography electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HPLC-ESI-MS) and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). The results elucidated that these compounds were composed of prodelphinidin (75%) and procyanidin (25%) with a degree of polymerization (DP) up to the 20-mers. They were proved to be remarkable, reversible and mixed competitive inhibitors of tyrosinase according to results from enzyme experiments. The IC50 values were calculated to be 23.6 ± 1.2 and 7.0 ± 0.2 μg mL−1 for the monophenolase and diphenolase activities, respectively. In addition, the proanthocyanidins had a good inhibitory effect on cell proliferation, cellular tyrosinase activity and melanin production of B16 mouse melanoma cells. Chelation between the hydroxyl group on the B ring of the proanthocyanidins and dicopper irons of the enzyme provided one of the feasible mechanisms for the inhibition on the basis of fluorescence quenching and molecular docking analyses. This research would supply the scientific basis to these compounds application in the pharmaceutical, insecticides, and preservative fields.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...