Apricot and other seed stones: amygdalin content and the potential to obtain antioxidant, angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitor and hypocholesterolemic peptides
Abstract
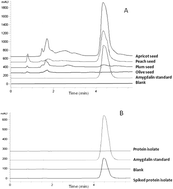
Stones from olives and Prunus genus fruits are cheap and sustainable sources of proteins and could be potential sources of bioactive peptides. The main limitation to the use of these seeds is the presence of amygdalin. This work proposes to determine amygdalin in olive and Prunus seeds and in protein isolates obtained from them. Moreover, antioxidant, angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, and hypocholesterolemic properties will be evaluated in hydrolysates obtained from these seeds. Despite some seeds contained amygdalin, all protein isolates were free of this substance. Two different procedures to obtain bioactive peptides from protein isolates were examined: gastrointestinal digestion and processing with Alcalase, Flavourzyme or Thermolysin. Higher antioxidant, ACE inhibitor and hypocholesterolemic activities were observed when proteins were processed with Alcalase, Flavourzyme or Thermolysin. The highest antioxidant and ACE inhibitor capacities were observed for the Prunus genus seed hydrolysates while the highest capacity to reduce micellar cholesterol solubility was observed for the apricot and olive seed hydrolysates.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...