Enhancement of ACE and prolyl oligopeptidase inhibitory potency of protein hydrolysates from sardine and tuna by-products by simulated gastrointestinal digestion
Abstract
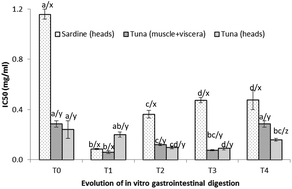
This work was focused on the study of the bioactive potential of three fish protein hydrolysates, one of them prepared from industrial sardine by-products (head and viscera) and the others from tuna by-products (head, and muscle and viscera). These protein hydrolysates exhibited moderate ability to inhibit Angiotensin Converting Enzyme or ACE (IC50 between 0.24–1.16 mg dry weight per ml) and prolyl oligopeptidase or PO (IC50 between 3.30–9.57 mg ml−1), those obtained from tuna by-products being the most effective. Overall, ACE- and PO-inhibiting activities were enhanced by sequential nanofiltration through 3 and 1 kDa MWCO membranes (IC50 between 0.02–0.16 mg ml−1 (ACE) and 1.10–4.21 mg ml−1 (PO)). The inhibitory properties of the hydrolysates were greatly improved by in vitro gastric digestion, and were barely affected by further intestinal digestion. The digested tuna hydrolysates, mainly that from heads, proved to be the best source of PO- and ACE- inhibiting molecules (IC50 = 0.16 mg ml−1 (ACE) and 1.04 mg ml−1 (PO)) and could be potential new ingredients in food with interest in the prevention or treatment of cardiovascular and neurological diseases.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...