Lactobacillus plantarum NCU116 attenuates cyclophosphamide-induced intestinal mucosal injury, metabolism and intestinal microbiota disorders in mice
Abstract
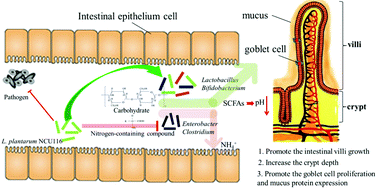
Anticancer drugs at high doses often damage the intestinal mucosa and metabolism. Lactobacillus plantarum NCU116 (NCU116) isolated from pickled vegetables was orally given to cyclophosphamide-treated mice to determine its effects on intestinal mucosal injury, nutrient metabolism and colon microbiota, and investigate the mechanisms accounting for its effects. Mice treated with the bacterium were found to favorably recover intestine morphology of villus height and crypt depth, and have improved mucins expression and quantity of goblet cells, as well as intestinal metabolism by increasing the level of short-chain fatty acids and reducing the concentration of ammonia in the colon feces. In addition, NCU116-treated mice showed a higher diversity of colonic microbiota than the group without bacterium supplementation. The number of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium in the mouse colon was increased after bacterium intake, which decreased the number of potentially pathogenic bacteria, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas. These results indicated that NCU116 could be of significant advantage in reducing intestinal mucosal injury and improving the intestinal metabolism and the intestinal microbiota.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...