In vitro fermentation of chewed mango and banana: particle size, starch and vascular fibre effects†
Abstract
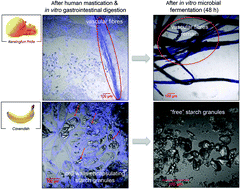
Fruits (and vegetables) contain cellular structures that are not degraded by human digestive enzymes. Therefore, the structure of the insoluble fraction of swallowed fruits is mostly retained until intestinal microbial fermentation. In vitro fermentation of mango and banana cell structures, which survived in vivo mastication and in vitro gastrointestinal digestion, were incubated with porcine faecal inoculum and showed intensive metabolic activity. This included degradation of cell walls, leading to the release of encapsulated cell contents for further microbial metabolism. Production of cumulative gas, short chain fatty acids and ammonia were greater for mango than for banana. Microscopic and spectroscopic analyses showed this was due to a major fermentation-resistant starch fraction present in banana, that was absent in mango. This study demonstrated distinctive differences in the fermentability of banana and mango, reflecting a preferential degradation of (parenchyma) fleshy cell walls over resistant starch in banana, and the thick cellulosic vascular fibres in mango.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...