Food derived microRNAs
Abstract
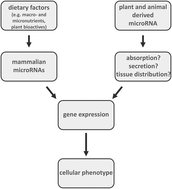
Foods provide fats, carbohydrates, and proteins as well as vitamins, minerals and trace elements. These dietary factors may influence cellular processes by regulating endogenous microRNA expression. MicroRNAs are non-coding regulatory molecules which affect gene expression at the post transcriptional level. It has been shown that plant and animal derived foods also contain microRNA. Yet, it is unclear if and to what extent plant and animal food derived microRNAs are absorbed by mammals. Thus, future studies need to better address absorption, tissue distribution and function of dietary plant and animal derived microRNAs in the context of human health and disease.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...